Over 2,000 Participants Received Irregular Heart Rhythm Notification in Apple Watch Study
Stanford Medicine researchers presented their findings of the Apple Heart Study at the American College of Cardiology's 68th Annual Scientific Session and Expo in New Orleans today, as noted by Apple in a press release.
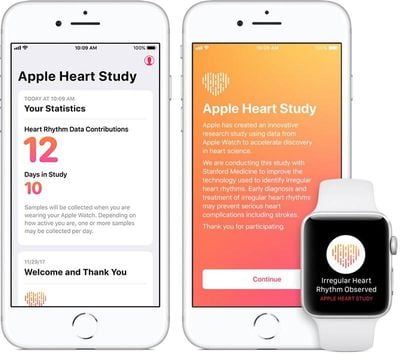
Apple and Stanford created the study to evaluate the Apple Watch's irregular heart rhythm notification feature, which occasionally checks the wearer's heart rhythm in the background and sends a notification if an irregular heart rhythm appears to be suggestive of atrial fibrillation.
419,093 people across the United States participated in the study. As part of the study, if an irregular heart rhythm was identified, participants received a notification on their Apple Watch and iPhone, a phone consultation with a doctor, and an ECG patch for additional monitoring.
Study results showed 0.5 percent of participants - approximately 2,095 people - received an irregular heart rhythm notification. Apple says "many participants sought medical advice following their irregular rhythm notification."
Apple COO Jeff Williams:
We are proud to work with Stanford Medicine as they conduct this important research and look forward to learning more about the impact of Apple Watch alongside the medical community. We hope consumers will continue to gain useful and actionable information about their heart health through Apple Watch.
Apple announced the Heart Study in collaboration with Stanford back in November 2017 and stopped accepting new participants in August 2018.
Popular Stories
Apple will launch its new iPhone 17 series in two months, and the iPhone 17 Pro models are expected to get a new design for the rear casing and the camera area. But more significant changes to the lineup are not expected until next year, when the iPhone 18 models arrive.
If you're thinking of trading in your iPhone for this year's latest, consider the following features rumored to be coming...
In select U.S. states, residents can add their driver's license or state ID to the Wallet app on the iPhone and Apple Watch, providing a convenient and contactless way to display proof of identity or age at select airports and businesses, and in select apps.
Unfortunately, this feature continues to roll out very slowly since it was announced in 2021, with only nine U.S. states, Puerto Rico,...
Since the iPhone X in 2017, all of Apple's highest-end iPhone models have featured either stainless steel or titanium frames, but it has now been rumored that this design decision will be coming to an end with the iPhone 17 Pro models later this year.
In a post on Chinese social media platform Weibo today, the account Instant Digital said that the iPhone 17 Pro models will have an aluminum...
Three out of four iPhone 17 models will feature more RAM than the equivalent iPhone 16 models, according to a new leak that aligns with previous rumors.
The all-new iPhone 17 Air, the iPhone 17 Pro, and the iPhone 17 Pro Max will each be equipped with 12GB of RAM, according to Fixed Focus Digital, an account with more than two million followers on Chinese social media platform Weibo. The...
Apple is expanding the ability to add an Apple Account Card to the Wallet app to more countries, according to backend Apple Pay changes.
With iOS 15.5, Apple updated the Wallet app to allow users to add an Apple Account Card, which displays the Apple credit balance associated with an Apple ID.
If you receive an Apple gift card, for example, it is added to an Apple Account that is also...
Apple does not plan to refresh any Macs with updated M5 chips in 2025, according to Bloomberg's Mark Gurman. Updated MacBook Air and MacBook Pro models are now planned for the first half of 2026.
Gurman previously said that Apple would debut the M5 MacBook Pro models in late 2025, but his newest report suggests that Apple is "considering" pushing them back to 2026. Apple is now said to be...
Apple is continuing to refine and update iOS 26, and beta three features smaller changes than we saw in beta 2, plus further tweaks to the Liquid Glass design. Apple is gearing up for the next phase of beta testing, and the company has promised that a public beta is set to come out in July.
Transparency
In some apps like Apple Music, Podcasts, and the App Store, Apple has toned down the...
If you pay for iCloud storage on your iPhone, did you know that Apple offers you five perks beyond the extra storage space, at no additional cost?
Here are the perks included with all iCloud+ plans:Private Relay keeps your Safari browsing history entirely private from network providers, websites, and even Apple.
Hide My Email generates unique, random email addresses whenever needed.
Hom...