Apple Once Again Blocks Java 7 Web Plug-in
Earlier this month, Apple took the unusual step of remotely blocking Oracle's Java 7 browser plug-in due to a major security vulnerability, using the "Xprotect" anti-malware system built into OS X to enforce a minimum version number that had yet to be released. Within days, Oracle updated Java to address the issue, with the new version number making the Java plug-in usable on OS X systems once more.
As noted by French site MacGeneration [Google translation] and the Apple discussion forums, Apple has once again blocked the Java 7 plug-in using Xprotect.
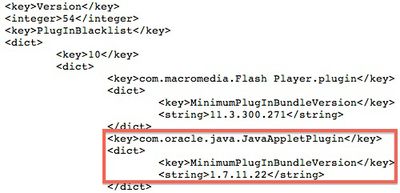
The updated blacklist enforces a minimum Java plug-in version of 1.7.0_11-b22, while the latest version of the plug-in is 1.7.0_11-b21.
The exact reason for Apple's renewed block on the Java plug-in is unknown although reports immediately following the release of Update 11 earlier this month indicated that it fixed only one of the two bugs that contributed to the security vulnerability. In the wake of that news, cybersecurity officials recommended that most users disable Java even with the up-to-date plug-in installed.
Oracle Security Alert CVE-2013-0422 states that Java 7 Update 11 addresses this (CVE-2013-0422) and an equally severe, but distinct vulnerability (CVE-2012-3174). Immunity has indicated that only the reflection vulnerability has been fixed and that the JMX MBean vulnerability remains. Java 7u11 sets the default Java security settings to "High" so that users will be prompted before running unsigned or self-signed Java applets.
Unless it is absolutely necessary to run Java in web browsers, disable it as described below, even after updating to 7u11. This will help mitigate other Java vulnerabilities that may be discovered in the future.
If this continued issue is indeed the reason for the new block by Apple, it is unclear why the company waited several weeks to update its plug-in blacklist.
Popular Stories
Since the iPhone X in 2017, all of Apple's highest-end iPhone models have featured either stainless steel or titanium frames, but it has now been rumored that this design decision will be coming to an end with the iPhone 17 Pro models later this year.
In a post on Chinese social media platform Weibo today, the account Instant Digital said that the iPhone 17 Pro models will have an aluminum...
Apple is continuing to refine and update iOS 26, and beta three features smaller changes than we saw in beta 2, plus further tweaks to the Liquid Glass design. Apple is gearing up for the next phase of beta testing, and the company has promised that a public beta is set to come out in July.
Transparency
In some apps like Apple Music, Podcasts, and the App Store, Apple has toned down the...
The calendar has turned to July, meaning that 2025 is now more than half over. And while the summer months are often quiet for Apple, the company still has more than a dozen products coming later this year, according to rumors.
Below, we have outlined at least 15 new Apple products that are expected to launch later this year, along with key rumored features for each.
iPhone 17 Series
iPho...
Apple should unveil the iPhone 17 series in September, and there might be one bigger difference between the Pro and Pro Max models this year.
As always, the Pro Max model will be larger than the Pro model:iPhone 17 Pro: 6.3-inch display
iPhone 17 Pro Max: 6.9-inch displayGiven the Pro Max is physically larger than the Pro, it has more internal space, allowing for a larger battery and...
In 2020, Apple added a digital car key feature to its Wallet app, allowing users to lock, unlock, and start a compatible vehicle with an iPhone or Apple Watch. The feature is currently offered by select automakers, including Audi, BMW, Hyundai, Kia, Genesis, Mercedes-Benz, Volvo, and a handful of others, and it is set to expand further.
Apple has a web page with a list of vehicle models that ...
New renders today provide the best look yet relocated Apple logo and redesigned MagSafe magnet array of the iPhone 17 Pro and iPhone 17 Pro Max.
Image via Majin Bu.
Several of the design changes coming to the iPhone 17 Pro model have been rumored for some time, such as the elongated camera bump that spans the full width of the device, with the LiDAR Scanner and flash moving to the right side.
...
Apple's next-generation iPhone 17 Pro and iPhone 17 Pro Max are just over two months away, and there are plenty of rumors about the devices.
Below, we recap key changes rumored for the iPhone 17 Pro models.
Latest Rumors
These rumors surfaced in June and July:Apple logo repositioned: Apple's logo may have a lower position on the back of the iPhone 17 Pro models, compared to previous...
Apple is expanding the ability to add an Apple Account Card to the Wallet app to more countries, according to backend Apple Pay changes.
With iOS 15.5, Apple updated the Wallet app to allow users to add an Apple Account Card, which displays the Apple credit balance associated with an Apple ID.
If you receive an Apple gift card, for example, it is added to an Apple Account that is also...





















