Apple Updates Mountain Lion Developer Preview With New Security Features
Apple has issued a new update for Mountain Lion Developer Preview 4 via the Mac App Store. It was first noticed by Twitter user @Lhunar and introduces the new Mountain Lion Security Update system.
The new system does daily checks for security updates as Apple ramps up its security protocols in the next-generation operating system. Earlier this month, it was noticed that Apple had changed the language on its OS X marketing pages following the Flashback malware attack earlier this year.
The new security system in Mountain Lion -- including Gatekeeper and other features -- appears to be a significant expansion of the XProtect system that Apple has used in the past to try to thwart OS X malware.
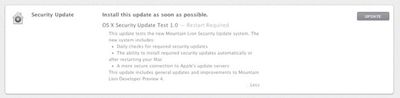
OS X Security Update Test 1.0 -- Restart Required
This update tests the new Mountain Lion Security Updates system. The new system includes:
- Daily Checks for required security updates
- The ability to install required security updates automatically or after restarting your Mac
- A more secure connection to Apple's update servers.
This update includes general updates and improvements to Mountain Lion Developer Preview 4.
The update weighs in at 1.16GB and is available to developers with Mountain Lion DP4 installed via the Mac App Store.
Popular Stories
Apple will launch its new iPhone 17 series in two months, and the iPhone 17 Pro models are expected to get a new design for the rear casing and the camera area. But more significant changes to the lineup are not expected until next year, when the iPhone 18 models arrive.
If you're thinking of trading in your iPhone for this year's latest, consider the following features rumored to be coming...
In select U.S. states, residents can add their driver's license or state ID to the Wallet app on the iPhone and Apple Watch, providing a convenient and contactless way to display proof of identity or age at select airports and businesses, and in select apps.
Unfortunately, this feature continues to roll out very slowly since it was announced in 2021, with only nine U.S. states, Puerto Rico,...
Apple does not plan to refresh any Macs with updated M5 chips in 2025, according to Bloomberg's Mark Gurman. Updated MacBook Air and MacBook Pro models are now planned for the first half of 2026.
Gurman previously said that Apple would debut the M5 MacBook Pro models in late 2025, but his newest report suggests that Apple is "considering" pushing them back to 2026. Apple is now said to be...
Three out of four iPhone 17 models will feature more RAM than the equivalent iPhone 16 models, according to a new leak that aligns with previous rumors.
The all-new iPhone 17 Air, the iPhone 17 Pro, and the iPhone 17 Pro Max will each be equipped with 12GB of RAM, according to Fixed Focus Digital, an account with more than two million followers on Chinese social media platform Weibo. The...
Since the iPhone X in 2017, all of Apple's highest-end iPhone models have featured either stainless steel or titanium frames, but it has now been rumored that this design decision will be coming to an end with the iPhone 17 Pro models later this year.
In a post on Chinese social media platform Weibo today, the account Instant Digital said that the iPhone 17 Pro models will have an aluminum...
A new Apple TV is expected to be released later this year, and a handful of new features and changes have been rumored for the device.
Below, we recap what to expect from the next Apple TV, according to rumors.
Rumors
Faster Wi-Fi Support
The next Apple TV will be equipped with Apple's own combined Wi-Fi and Bluetooth chip, according to Bloomberg's Mark Gurman. He said the chip supports ...
Production of foldable OLED displays for Apple's first foldable iPhone have begun ahead of its expected launch next year, Korea's ETNews reports.
The first foldable iPhone's displays are being produced by Samsung Display, who are establishing a production line dedicated to the upcoming Apple device its A3 factory in Asan, Chungcheongnam-do. The production line will make displays exclusively...
iPhone 17 Pro and iPhone 17 Pro Max models with displays made by BOE will be sold exclusively in China, according to a new report.
Last week, it emerged that Chinese display manufacturer BOE was aggressively ramping up its OLED production capacity for future iPhone models as part of a plan to recapture a major role in Apple's supply chain.
Now, tech news aggregator Jukan Choi reports...