While Steve Jobs famously panned the idea of a stylus for the iPhone at the device's unveiling in January 2007, Apple has continued researching ideas for stylus-based input, if only as part of continued reevaluation of how users interact with their devices and how technology will change those interactions over time. Toward that end, Unwired View highlights a pair of Apple patent applications filed in late 2010 and published today addressing optical and haptic stylus concepts.
Apple's idea for an optical stylus takes advantage of a tiny camera on the tip of the pen that would allow it to track patterns on a device's screen that are invisible to the user's eye. The stylus could also incorporate other sensors such as pressure sensors, accelerometers, and gyroscopes to help determine orientation and movement.
In some embodiments, a stylus is provided with an optical sensor, such as a camera, that is used in determining a location and movement of the stylus relative to a touch screen display of a computing device. It should be appreciated, however, that displays other than touch screens may be implemented in some embodiments. The optical stylus may be configured to transmit the location and movement to the computing device. In some embodiments, the optical stylus may be configured to process and/or filter the location and movement information prior to transmission, whereas in other embodiments, raw data may be transmitted.
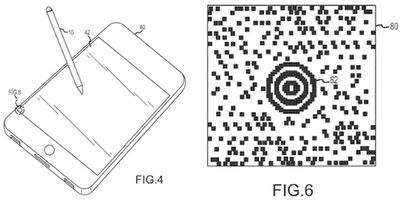
Apple's generic iPhone stylus concept with enlarged view of encoding pattern for tracking movement
Alternatively, Apple suggests that it could incorporate haptic feedback to allow users to gain a tactile feel for the content on a device's screen via a stylus. Apple has researched haptics for quite some time, and the patent application published today describes how a haptic actuator embedded in the stylus could receive signals from a device to help users gain a tactile feel for the context of their onscreen input.
Generally, input devices do not provide haptic feedback to a user in response to interactions with the input device. The user can typically only feel the rigid surface of the touch screen, making it difficult to find icons, hyperlinks, text boxes, or other user-selectable input elements on the display. An input device capable of generating haptic feedback may help a user navigate content displayed on the display screen, and may further serve to enhance the content of various applications by creating a more appealing and realistic user interface. "Haptic feedback" may be any tactile feedback. Examples include forces, vibrations, and/or motions that may be sensed by the user.
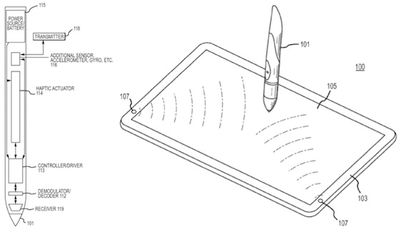
Apple's concept for stylus with haptic feedback
There has been essentially no evidence that Apple is seriously looking at incorporating a stylus into its products, but it remains clear that the company is thinking about how such pen-based input could be used in novel ways.



















