In an interview with Popular Mechanics, Apple engineers Chris Ligtenberg and John Ternus have detailed some of the innovative cooling features included in the design of the Mac Pro and Pro Display XDR, both of which launched earlier this week.

In order to let the ridiculous processing power of the Mac Pro reach its potential without melting, Apple engineers had to find new ways to "exploit the laws of thermodynamics," according to the report.
For example, the active internal cooling consists of three axial fans in the front of the case and a blower in the rear, all of which had to be developed in-house because off-the-shelf fans would have been too loud.
"Years ago, we started redistributing the blades," explains Ligtenberg, Apple's senior director of product design. "They're still dynamically balanced, but they're actually randomized in terms of their BPF [blade pass frequency]. So you don't get huge harmonics that tend to be super annoying."

"That [solution is] borrowed almost entirely from automobile tires," Ligtenberg says. "There's a bit of math behind it, but you can create broadband noise instead of total noise with that technique."
Something loud but pleasantly pitched can be more tolerable than something quiet but irritating. "You can have something at a certain SPL [sound pressure level] that sounds really good, but you can have something that's actually at a lower SPL that grates on your nerves and sounds really awful," says John Ternus, VP of Hardware Engineering at Apple and head of the Pro and Pro Display's development. "We want to get really great performance where, you either can't hear it, or if you can hear it, it's kind of a pleasant noise. A ton of analysis goes into figuring out how to optimize for that."
Apple hopes Mac Pro users won't even be aware of the fan activity inside, but it's the conspicuous grids of bored metal divots on the front and back of the case and the rear of the Pro Display that provide the passive cooling. "[The pattern] gives us a lot of surface area, which is hugely beneficial," Ternus says.
The Pro Display has fans for specific components, but the bored metal holes are what keeps that panel of LEDs cool enough to run so bright. It wasn't possible to use a traditional finned enclosure heatsink, because the monitor can be used in both portrait and landscape.
Rotating the display 90 degrees would reduce with the air flow through fins, but the hemispherical holes work the same regardless of which way is up. "[For the Display] we wanted free [air] flow through the channels, no matter the orientation," says Ternus.
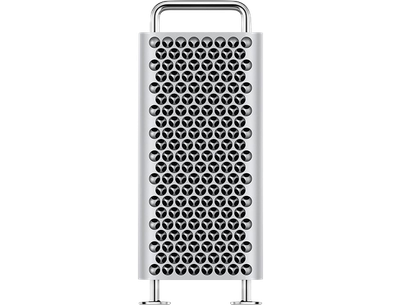
According to Apple, the reworked "cheese grater" look achieves around 20 percent more airflow compared to the Power Mac G5 that preceded it.
Apple is accepting orders for the Mac Pro (starting at $5,999) and the Pro Display XDR ($4,999) on its website, with Mac Pro delivery estimates at one to two weeks after an order is placed.



















